FMGE exam pattern
1. What is FMGE:
To understand the MCI Exam pattern, we must know that what MCI exam is all about. Every year, the MCI Screening Exam, also known as the Foreign Medical Graduates Examination (FMGE) is conducted twice a year. This is a licensure examination, mandatory for Indian nationals who want to practice medicine in India after completing their medical degree from abroad.
Click here for detailed info about FMGE Exam
2. Duration of exam:
FMGE Exam is generally conducted in June
and in December. It consists of two parts. Both the modules are conducted on a
single day
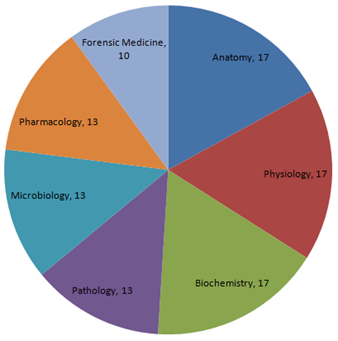
Module 1. This module consists of 150 MCQs and the duration is 2 hrs 30 mins. It starts at 9:00 AM. This module covers mainly pre and para-clinical subjects. Subjects covered are:
1. Anatomy
2.
Physiology
3.
Biochemistry
4.
Pathology
5.
Microbiology
6.
Pharmacology
7. Forensic Medicine
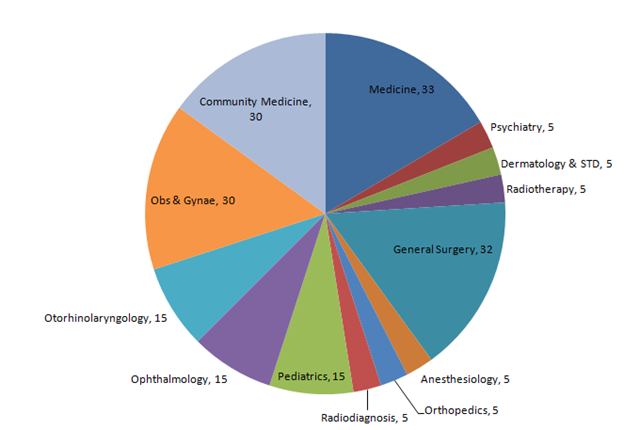
Module 2. This module comprises 200 MCQs. This is also for 2 hrs 30 mins and starts at 2:30 PM. This module covers Clinical Subjects. Subjects covered in this module are :
1.
Medicine & Allied Subjects
(I) Medicine
(Ii) Psychiatry
(Iii) Dermatology
& Std
(Iv) Radiotherapy
2.
General Surgery & Allied Subjects
(I) General Surgery
(Ii)
Anesthesiology
(Iii) Orthopedics
(Iv)
Radiodiagnosis
3.
Pediatrics
4.
Ophthalmology
5.
Otorhinolaryngology
6.
Obstetrics & Gynaecology
7. Community Medicine
- Detailed syllabus of FMGE / MCI Screening exam
Syllabus of FMGE exam is same as the
syllabus of MBBS prescribed by MCI. Details list of topics to be covered is as
follows:
ANATOMY
1. General Anatomy : Basictissuestobody,Terminology & Nomenclature
2. Elements of Anatomy : Osteology, Arthrology, Myology, Angiology,
Neurology
3. Regional Anatomy : Upper limb, Lower limb Thorax-including diaphragm
Abdomen and Pelvis, Head, Neck, Brain and Spinal cord
4. Embryology : Development of individual organs and systems, Postnatal
growth & development
5. Histology : General Histology Microanatomy of individualorgans &
systems
6. Human Genetics : Principles of Human genetics and Molecular biology
7. Radiological Anatomy : Skiagrams, Special X-rays, Principles of
imaging techniques.
8. Surface Anatomy : In cadavers, in the living
9. Sectional Anatomy : Thorax, Abdomen, Head, Neck and Brain
PHYSIOLOGY
1. General Physiology
2. Body fluids – Blood
3. Nerve and Muscle
4. Gastrointestinal Tract
5. Kidney
6. Skin and Body temperature
7. Endocrine Glands
8. Reproduction
9. Cardiovascular System
10. Respiratory System
11. Central Nervous Systems
12. Special Senses
BIOCHEMISTRY
1. Cell and Sub-cellular structures
2. Hydrogen Ion concentration Acid, Bases, Buffers, Handerson-Haselbach
equation
3. Isotopes and their Application
4. Carbohydrates
5. Amino Acids, Peptides and Proteins
6. Lipids
7. Nuclear Acids
8. Enzymes
9. Vitamins
10. Biological Oxidation
11. Digestion and Absorption from GI Tract
12. Intermediary Metabolism
13. Carbohydrate Metabolism
14. Lipid Metabolism
15. Protein and Amino Acid Metabolism
16. Purine and Primidine Metabolism
17. Minerals
18. Biochemical Genetics and Protein Biosynthesis
19. Tissue Biochemistry
20. Liver Functions
21. Nutrition and Energy Metabolism
PATHOLOGY
1. Cell injury
2. Inflammation and Repair
3. Immunopathology
4. Infectious diseases
5. Circulatory disturbances
6. Growth disturbances and Neoplasia
7. Nutritional and other disorders
8. Genetic disorder
9. Haematology
10. Cardiovascular Pathology
11. Respiratory Pathology
12. Pathology of Kidney and urinary Tract
13. Hepato-Biliary Pathology
14. Lymphoreticular System / Spleen
15. Reproductive System (male & female)
16. Diseases of the Breast
17. Musculoskeletal System
18. Endocrine pathology
19. Neuropathology
20. Dermato-Pathology
21. Ocular Pathology
MICROBIOLOGY
1. General Microbiology
2. Immunology
3. Bacteriology
4. General Virology
5. Systemic Virology
6. Mycology
7. Parasitology
8. Clinical / Applied Microbiology
PHARMACOLOGY
1. General Pharmacology
2. Autonomic Nervous System
3. Cardio-vascular System
4. Diuretics
5. Drugs affecting blood and blood formation
6. Autocoids and related drugs
7. Respiratory System
8. Gastro-intestinal System
9. Endocrine pharmacology
10. Central Nervous System
11. Psychopharmacology
12. Drugs in Anaesthetic practice
13. Chemotherapy
14. Toxicology
15. Clinical Pharmacology and Rational drug use
FORENSIC MEDICINE
1. Definitions
2. Courts of India
3. Court procedures
4. Medical Certifications & medico-legal reports including dying
declaration
5. Death
6. Changes after death
7. Inquest by police, magistrate and coroner
8. Identification
9. Examination of mutilated human remains
10. Medico-legal autopsies
11. Mechanical injuries and wounds
12. Examination of an injury case
13. Injuries due to physical agents & their medico legal importance
14. Asphyxial death
15. Death due to malnutrition, neglect battered babies
16. Dowry death
17. Virginity, sexual offences, sexual perversions
18. Legitimacy
19. Pregnancy and delivery
20. Infanticide
21. Biological fluids
22. Seminal stains
23. Forensic Psychiatry
24. Medical Jurisprudence
25. Toxicology
GENERAL SURGERY
1. Hemorrhage and shock
2. Fluid, electrolyte and Acid balance, nutrition
3. Skin tumours, burns, skin grafting
4. Arterial diseases
5. Venous diseases
6. Lymphatic and Lymph nodes
7. Wounds
8. Specific and non-specific injections
9. Tumors, Cysts, Ulcers and Sinuses and Fistulae
10. Infections of Hand and Foot
11. Diseases of muscle, tendons, bursae and fascia
12. Hernia
13. Umbilical granuloma, fistula, adenoma
14. Abdominal Wall
15. Face, Teeth, Gums, Mouth, Tongue, Salivary glands, Neck
16. Thyroid Glands, Thyroglossal Tract and Endocrines
17. Breast
18. Sympathetic System
19. Cranio-Cerebral injuries
20. Brain, Nerves
21. Genito-Urinary System
22. Kidneys and Ureters
23. Urinary Bladder
24. Prostrate
25. Urethra
26. Penis, Testis and Scrotum
27. Vasectomy and Recanalisation
28. Cardiothoracis System
29. Oesophagus, Stomach and Duodenum
30. Spleen, Liver, Gall Bladder and bile ducts
31. Pancreas
32. Peritoneum
33. Intestines, intestinal obstruction
34. Appendix
35. Rectum and Anal Canal
ANESTHESIA
1. Anatomy of upper airway
2. Physiology of Respiration O2/CO2 transport. Methods of oxygen
therapy.
3. Pre-operative evaluation/pre-medication
4. Anaesthetic agents, stages of Anaesthesia
5. Principles and mechanism of administration of general anaesthetics,
balanced Anaesthesia
6. IPPV, Endotracheal Intubations
7. Muscle Relaxants
8. Spinal/Epidural Anesthesia
9. Local Anesthesia
10. Cardiopulmonary resuscitation basic, use of simple ventilators
11. Monitoring
12. ICU, role of anaesthesiologist in ICU
13. Shock
14. Blood Transfusion and Fluid Electoral Balance
15. Sites of respiratory obstruction and management of airway in an
unconscious patient
16. Poisoning
17. Role of anaesthesiologist in acute and chronic relief.
ORTHOPEDICS
1. Traumatology
- Injuries of bones and joints Injuries of Lower
Extremity - Injuries of the Spine Vascular Injuries
2. Cold Orthopedics
3. Regional Conditions
4. Neuro-Muscular Disorder
5. Bone and Joint Tuberculosis
6. Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
RADIO- DIAGNOSIS
1. Respiratory System
2. Cardiovascular System
3. Gastrointestinal System
4. Obstetrics &Gynaecology
5. Skeletal System
6. Central Nervous System
7. Excretory System
RADIOTHERAPY
1. Principles of Radiotherapy
2. Principles of Chemotherapy
3. Prevention and Early diagnosis of Cancer
4. Principles of Nuclear medicine
5. Common radiation reactions and management
6. Radiotherapy and chemotherapy in commonly seen cancers
7. Radio-isotopes in diagnosis and therapy
PAEDIATRICS
1. Vital statistics
2. Neonatology
3. Growth & Development
4. Nutrition
5. Infections
6. Genetics
7. Pediatric Emergencies
8. Central Nervous System
9. Gastrenterology
10. Nephrology
11. Endocrinology
12. Respiratory System
MEDICINE
1. Clinical Methods in the practice of Medicine
2. Common symptoms of disease
3. Nutrition/Exposure to Physical & Chemical Agents
4. Infections
5. Haematology
6. Respiratory System
7. Cardio-Vascular System
8. Gartro-Intestinal Tract
9. Emergency Medicine
10. Neurological System
11. Nephrology & Urinary system connected to Tissue Disorders
12. Endocrine System
13. Geriatrics
TUBERCULOSIS AND RESPIRATORY
DISEASES
Diagnosis and management of common ailments affecting the chest
with special emphasis on management and
prevention of Tuberculosis and National Tuberculosis Control Program.
PSYCHIATRY
1. History aspects and diagnosis & treatment of mental illness
2. Conduction of Mental Status Examination
3. Behavioral Sciences
4. Different psychoses Clinical features, diagnosis and management of :
5. Schizophrenia
6. Mania and depression
7. Anxiety disorders and hysteria
8. Dementia
9. Alcoholism
10. Drug Abuse
11. Psychiatric emergencies
12. Clinical features, diagnosis and management of psychiatric
disorders of childhood and adolescence
13. Personality disorder
DERMATOLOGY AND SEXUALLY
TRANSMITTED DISEASES
1. Dermatological therapy
2. Lichen Planus
3. Diseases caused by Nutritional and Environmental Factors
4. Infective Disorders
5. Melanocytes, pigment metabolism and other disorders of Pigmentation
6. Allergic Disorders
7. Dermatitis and Eczema
8. Vesiculobullous Diseases
9. Alopecia and Hirsutism
10. Structure and functions of Sebaceous glands and Disease
11. Leprosy
12. Psorasis
13. STD
OPHTHALMOLOGY
1. Basic sciences – Anatomy, Physiology, Pharmacology, Pathology,
Elementary Optics, Diseases of the Eye
2. Conjunctiva
3. Cornea
4. Sclera
5. Uveal Tract
6. Lens
7. Vitreous
8. Glaucoma
9. Retina
10. Optic Nerve
11. Intra-Occular Tumors
12. Squint
13. Orbit
14. Lacrimal System
15. Lids
16. Refractive Errors
17. Injuries
18. Ophthalmic Surgery
19. Community Ophthalmology
20. Miscellaneous
OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY
1. Diseases of the Ear
2. Diseases of Nose and Para Nasal sinuses
3. Diseases of Nasopharynx
4. Diseases of Trachea
5. Oesophagus
OBSTETRICS AND GYNECOLOGY
1. Anatomy of the Female reproductive Tract
2. Physiology of conception
3. Development of foetus and placenta
4. Diagnosis of pregnancy
5. Maternal changes in pregnancy
6. Antenatal care
7. Abnormal obstetrics
8. Normal labour
9. Normal puerparium
10. Breast Feeding
11. Care of new born
12. Medical termination of pregnancy
13. Family planning
14. Operative obstetrics
15. Post caesarian pregnancy
16. Pharmaco therapeutics in obstetrics
17. Safe motherhood
18. Maternal morbidity and morality
19. Medico legal aspects
20. RCH
21. Current topics
22. Vaginal discharge
23. Menstrual disorder
24. Fertility, infertility
25. Endometriosis and allied states
26. Genital injuries and fistulae
27. Genital infections
28. Genital prolapse
29. Tumours
30. Carcinomia
31. Radiotherapy in gynaecology
32. Chemotherapy in gynaecology
33. Endoscopy
34. Diseases of breast
35. Operative gynaecology
COMMUNITY MEDICINE
1. Evaluation of Public Health and Concepts of Health
2. Environment and Health
3. Health Education
4. Nutrition and Dietetics
5. Occupational Health
6. Medical Sociology and Community Mental Health
7. Fundamentals of Biostatistics
8. Basic Epidemiology
9. Epidemiology of Specific Diseases
10. Communicable and Non-Communicable Diseases
11. Demography
12. Reproductive and Child Health
13. School Health
14. Urban Health
15. Health System in India
16. Health Planning and Management including Disaster Management
17. International Health
Please
note this is not exhaustive list of topics. For detailed document visit https://www.mciindia.org
3. Marking of exam
FMGE Exam consists of 300 MCQs, each MCQ of
1 Mark. Total marks are 300 out of which, to clear the exam, one has to obtain
150 marks. There is no negative marking in FMGE Exam.
4. Sample mock test download
Download Sample mock test of FMGE with explanations from here

